This article focuses on how eramba can help with ISO 27001, Annex A. These controls are what ISO calls “possible information security controls” you could use to treat the Risks you in theory have identified in 6.1.2 and are willing to treat under 6.1.3
Note: we have another guide that focus on ISO 27001 requirements
ISO has multiple technical, physical related, controls which of course eramba can not help (eramba can not manage your firewalls for example). We have excluded such cases.
Note: Bear in mind that since all of these (technical) controls still need policies, procedures, standards, audits, etc and those are typically done with eramba.
Let’s dive into the ones eramba can directly help you with:
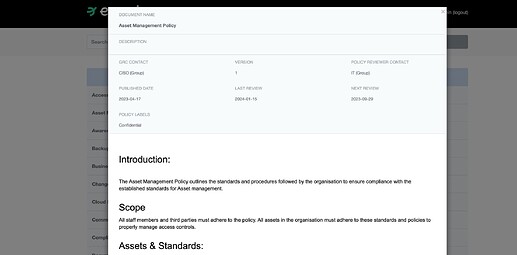
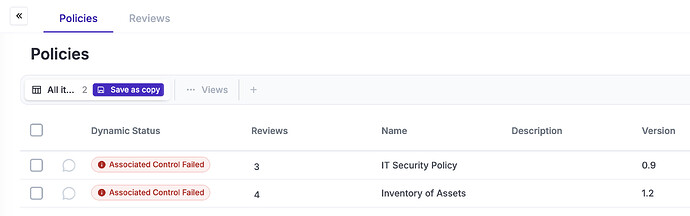
5.1 - Policies for information security
you need the paperwork (policies, etc) published to everyone, since eramba has all your policies you can also publish them on the “Policy Portal” eramba ships with.
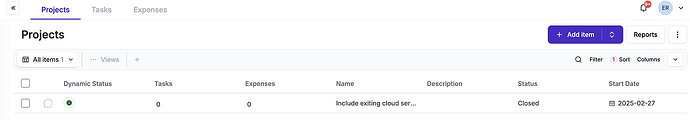
5.8 - Information security in project management
the projects that take place in your company should in theory consider security aspects, you can use the project module to document these projects in eramba directly.
The project module helps you define what your organisation will do IN THE FUTURE to deal with a problem (Risk, Compliance requirement, failed Control, failed Policy, Etc). The project module has owners, deadlines, tasks, Etc.
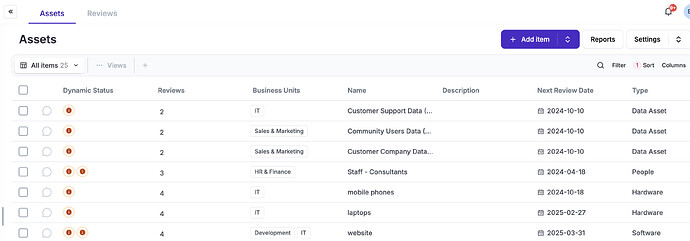
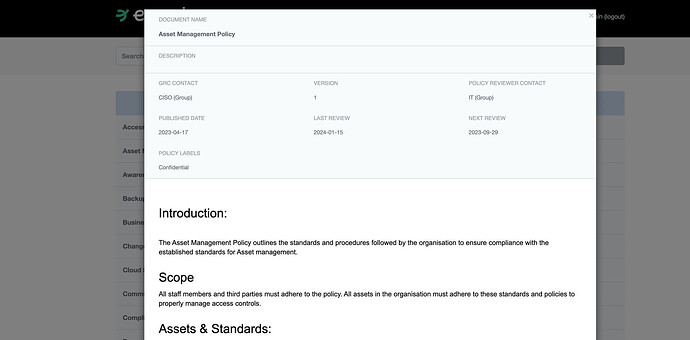
5.9 - Inventory of information and other associated assets
while eramba is not an inventory tool and iso is pretty clear that these inventories should be managed by each department in your organisation, you could still use the asset module for this.
The asset module allows you to document assets (computers, etc), classify them, review them and use them for Risk assessment purposes.
5.12 - Classification of information
As part of the Asset module, you can define your own classifications and apply them to each asset.
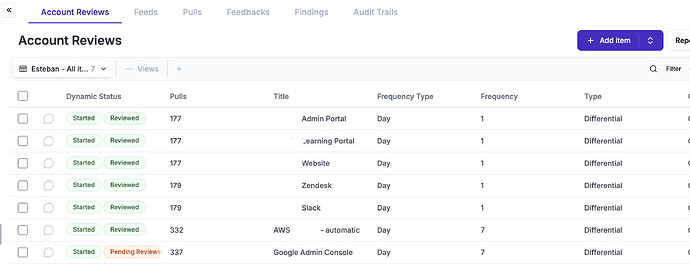
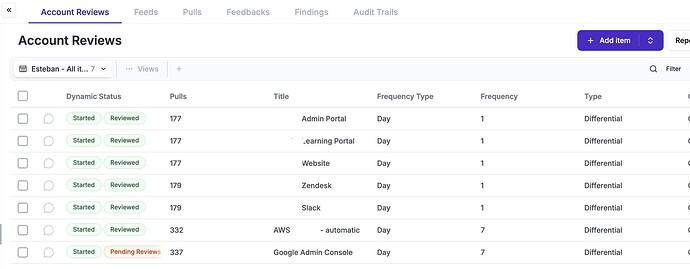
5.18 - Access rights
The Account Review module helps you to automatically pull accounts from systems and ask people on your organisation to review them.
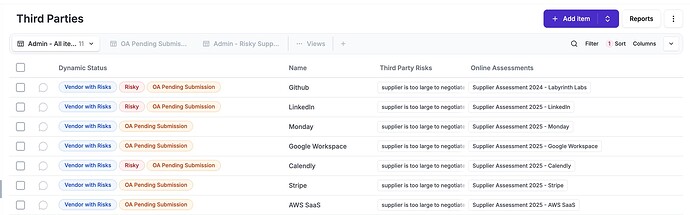
5.19 - Information security in supplier relationships
5.20 - Addressing information security within supplier agreements
5.21 - Managing information security in the information and commu- nication technology (ICT) supply chain
5.22 Monitoring, review and change management of supplier services
You can record all your suppliers at eramba’s third party module
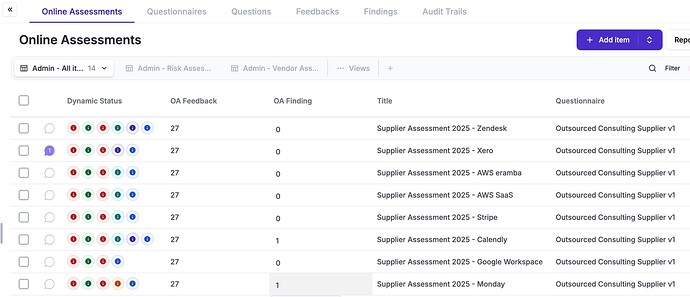
You can use the Online Assessment module to create custom made supplier questionnaires and submit them online. Recipients of these questionnaires will login to a portal and provide you with feedback.
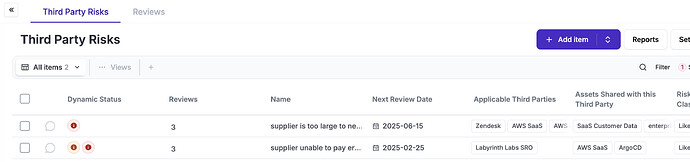
As part of the Risk modules, you can identify Third Party Risks and define there what issues could exist with them (along with their treatment).
The Risk module in eramba helps you identify, document, classify, review and treat Risks in your organisation, no matter what their origin is. This module is perfectly compatible with ISO and most International Risk frameworks.
5.24 - Information security incident management planning and preparation
5.25 - Assessment and decision on information security events
5.26 - Response to information security incidents
5.27 - Learning from information security incidents
5.28 - Collection of evidence
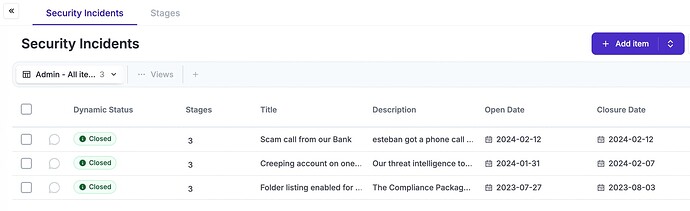
The idea here is that you record security incidents and systematically review them.
eramba has a built in Incident Management module that allows you to link incidents to risks (risks in theory have background information on potential incidents) and allow you systematically analyse incidents based on a user defined workflow.
5.30 - ICT readiness for business continuity
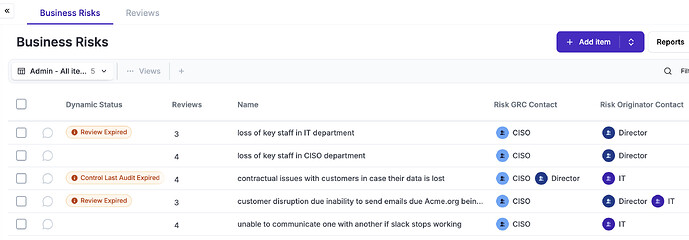
ISO expects you to identify continuity scenarios and where possible plans that can be used to somehow guarantee that these processes will continue working.
The risk module allows you to document business related Risks, with their corresponding continuity attributes (mto, rto, etc). These risks can be reviewed, classified, etc.
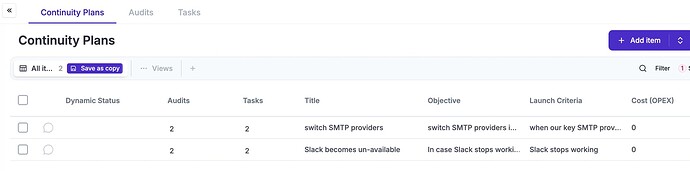
As part of the mitigation of these continuity events, in eramba you can define continuity plans.
The Continuity Plans module in eramba allows you to document continuity plans, their responsible, the plan tasks and also their testing methodology. eramba will help houy remember testing these plans using notifications and storing evidence that prives that you have completed such tests.
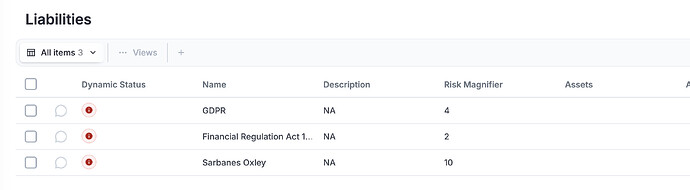
5.31 - Legal, statutory, regulatory and contractual requirements
You can document in eramba all your liabilities (that is how we call these things) and how they affect to your Risks.
5.33 - Protection of records
5.34 - Privacy and protection of personal identifiable information (PII)
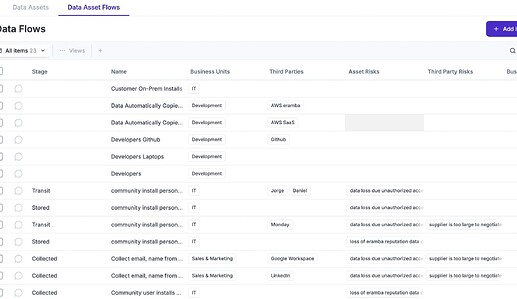
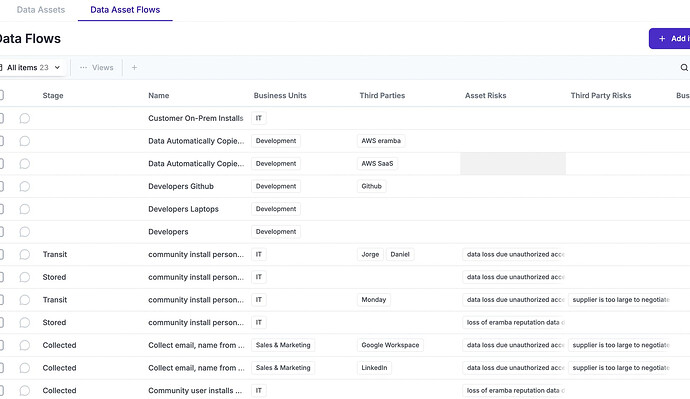
To protect data you first need to know it’s lifecycle (how is collected, transmitted, deleted, modified, etc) and for each one of these flows how is protected (controls) what risks exists, who is touching it, etc.
The Data Flow module helps you to document how data moves around the organisation and how is protected (or not). The module also let’s you document GDPR aspects of these flows. If you ever get asked how you protect data, then this is the module you need.
5.35 - Independent review of information security
The idea here is that someone audits your ISMS (risks, testing of controls, projects, management reviews, etc). This someone can not be you or someone that runs the ISMS or has an interest in making this ISMS look good. eramba has a strong traceability capability where all these things are documented and reviewed and this makes the auditor life much simpler, as its “all there”. You can adjust permissions for auditors to access data (without adding, deleting or editing) and easily let them do their work while you do yours.
5.36 - Compliance with policies, rules and standards for information security
Policies describe how “things should be done”, in eramba Internal Controls describe how things are done (based on policies) and these controls in eramba must be tested. If testing of controls pass, then you are meeting what document say you should do. If you don’t test you dont know if you meet policies requirements. If you controls testing do not pass then you know for a fact you dont meet requirements.
5.37 - Documented operating procedures
ISO want’s you to have as much documentation as feasible that explains how your ISMS runs, they also want you to make that public to the organisation on a need to know basis.
The policy portal as explained before does this in conjunction with the policy module.
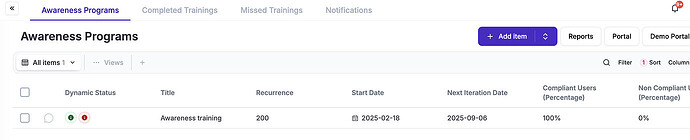
6.3 - Information security awareness,education and training
well people in the organisation needs to know about your ISMS, the more tailor made content for each department you can pull off the better.
The awareness program module in eramba helps you upload videos, disclaimer texts and multiple choice questionnaires and define audiences that must complete these trainings at regular intervals.
8.2 - Privileged access rights
Part of this obvious requirement is to “regularly, and after any organizational change, reviewing users working with privileged”, while (surprisingly) not explicit on the guidance from ISO, this also applies to 8.3 and 8.4.
The Account Review module helps you to automatically pull accounts from systems and ask people on your organisation to review them.
8.10 Information deletion
8.11 Data masking
8.12 Data leakage prevention
8.13 Information backup
In order to implement this control you need to understand what data you manage and how that is done, the flow module is therefore typically used for this control.
The Data Flow module helps you to document how data moves around the organisation and how is protected (or not). The module also let’s you document GDPR aspects of these flows. If you ever get asked how you protect data, then this is the module you need.
8.14 - Redundancy of information processing facilities
This requirement is a close cousin of 5.30 as you need to identify and plan what could be done in the case you find operational processes that could be disrupted.
The risk module allows you to document business related Risks, with their corresponding continuity attributes (mto, rto, etc). These risks can be reviewed, classified, etc.
As part of the mitigation of these continuity events, in eramba you can define continuity plans.
The Continuity Plans module in eramba allows you to document continuity plans, their responsible, the plan tasks and also their testing methodology. eramba will help houy remember testing these plans using notifications and storing evidence that prives that you have completed such tests.